Videos
Check out our tutorial video series.
Mastering Email Headers: Take control of your email communication with email envelopes. Analyze different fields and ensure secure exchanges.
The email header is a necessary part of every email exchange that has both functional and educational purposes. Learning to examine email headers can assist you in establishing secure email communication. So what email headers? Read on to find out.
Every email has a metadata attachment known as an email header that includes information about the sender, recipient, route, time, and other things. Information in the email's metadata is generated automatically, depending on how it was written and sent.
The instructions may vary slightly depending on your mailbox provider, but the metadata readability of Email Headers is consistent across all emailing platforms.
| Email Client | View Email Header |
|---|---|
| Gmail | In the email's top-right corner, look for a three-dot icon. Choose Show Original |
| Apple | In the upper-left corner of the panel, choose View. Then, choose All Headers under Message. |
| Webmail | On the More Menu, Click “Show Source.” |
| Hotmail | Right-click on the email option to bring up a menu. Click on View Message Source |
| Thunderbird | With email open, click on View Then, Select Message Source |
| Yahoo | Choose more on the panel above the email Select View Full Header |
| Outlook | Select Properties from the File menu after opening the email. Search the Internet for Email Headers by scrolling down. |
The Email Headers format consists of a separator character, a value identifier, and a field with a name that corresponds to it.
The from, to, subject, and date fields are the four main fields found in an email message header. The header also includes other technical information, including return-path, reply-to, message-id, and more; only date and form are required.
The word "from" denotes information about the sender, such as an address.
To display the names and, if applicable, email addresses of the CC and BCC recipients.
Delivered-To lists the name and address of the recipient as well as any additional addresses found in the CC and BCC. During delivery, a Deliver-To header is added, displaying the recipient's address who accepted the delivery.
The email's subject refers to the title the sender has provided in the subject line.
The optional Reply-To field is where a recipient will put their reply address.
The Content-Type field lets you know whether an email was sent in HTML, TXT, or another format.
Or
The recipient's email server automatically adds Return-Path and logs the original sender throughout the SMTP session. Bounces from the SMTP session go back to the Return-Path address.
Another authentication technique to confirm that the email was authorized by the domain owner is DKIM-Signature or DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). The email is signed digitally, and the sender's public key can be found in the DNS records for the sender's domain to confirm the sender's identity.
A server can store the outcomes of authentication verification in this field for later consumption by agents.
Senders use SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, as a method of authentication to specify the hosts that are permitted to send emails on the domain's behalf. To ensure that an email sent from a domain came from one of the hosts listed in the sender's DNS records, MTA verifies the sender's DNS records or PTR records.
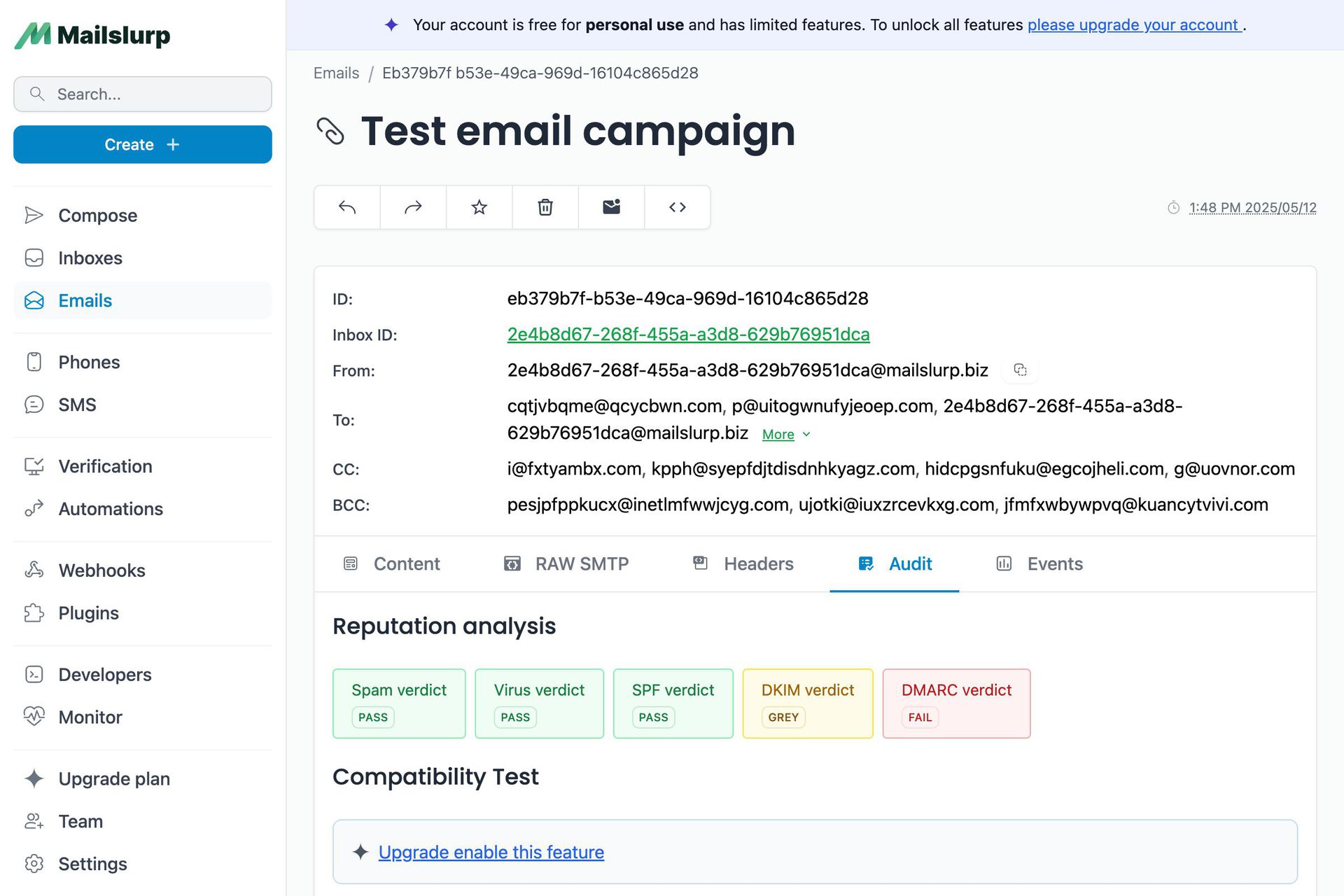
Utilizing programs like mailslurp Email Sandbox, email headers should be examined when testing emails.
You can inspect and debug emails in staging with mailslurp Email Sandbox without worrying about spamming recipients. And you can also view the original values of email headers for each test email you send to an Email Sandbox virtual inbox.
Other tools to work with Email Headers include;
Email headers confirm an email's legitimacy. Additionally, it is the most effective tool for locating, analyzing, and decoding information, preventing spam, phishing, and spoofing. Four key factors support the significance of email headers.
You can determine whether an email successfully reaches a recipient's inbox by understanding the Email Headers. This enables you to implement the necessary security precautions in order to enhance your sender reputation.
Check out our tutorial video series.
Email and SMS guides for automation and testing.
View github project code for multiple languages.
Latest posts from the MailSlurp team.
Test, build, and automate messaging with a free MailSlurp account.