Videos
Check out our tutorial video series.
Use inbound and outbound email in code, mail-clients, or online dashboard. Add attachments, configure webhooks and gain SMTP access.
MailSlurp is a powerful email service for developers, QA testers, and email marketers. Create real email addresses on demand and then send and receive emails at scale in any platform or context you choose. Emails can be sent and received in numerous ways with MailSlurp. This post will cover some common uses.
The key component of MailSlurp is the - a real email address that can be created and configured programmatically. The inbox type determines which sending and receiving methods are available. For SMTP and IMAP access ensure you use the inbox type. The same applies to domains if you are using a custom domain.
Login to the MailSlurp dashboard to create an inbox using the graphical interface.

Use the REST API or developer SDK clients to create mailboxes in code and tests. Here is an example using the MailSlurp Javascript client:
See the other SDK clients for examples in your preferred programming language.
You can send emails from any inbox you create in a variety of ways including the REST API, graphQL, SMTP and using the online mail client.
See the API documentation for more information.
Sending emails to recipients that have bounced in the past will throw an API error. To avoid this use the flag to filter out any known bad addresses when sending. If the email addresses are not already known then it is best to use the validation options below.
You can verify email address lists before sending or when you send using a validation filter. Here is how verify emails before sending:
To verify during sending you can pass a validation option that will either remove bad addresses after verification or throw an error:
Send emails using a pub/sub queue system to ensure delivery and enable recovery from failure. Use the sending options in the dashboard or in code:

To send with a queue in code use the following methods:
Emails send via a queue will be retried until delivery succeeds.
Use the job scheduler in MailSlurp to send emails at a given time or delay email sending.
One can also pass a timestamp to send at a given time:
See the schedule email guide.
Every inbox you create in MailSlurp can be controlled via SMTP. View the access details on the dashboard homepage:

Configure any SMTP client to use an inbox SMTP settings. Access the SMTP port, host, username and password using the method:
Read the SMTP tutorial for details.
Read the IMAP tutorial for details.
Upload attachments and compose emails in the MailSlurp dashboard.

MailSlurp runs SMTP mail servers that receive emails for your inbox email addresses. Emails are parsed and stored and made available via HTTP API, SMTP/IMAP, and online.
Have inbound emails sent to your server via secure HTTP/S webhooks backed by queues. Handle large inbound flow, respond to email events and recover from failures. Webhooks are the best way to process emails in production.

See webhook documentation to start using webhooks.
Email is an asynchronous system as emails that are sent need to time to arrive. MailSlurp provides methods to wait for emails to arrive and conditions to be met. This way your tests can wait until an expected email is received and assert against it.
See the wait for guide and email matching documentation.
Connect your SMTP client or IMAP mail software to MailSlurp using the SMTP/IMAP credentials assigned to each inbox. See the IMAP/SMTP documentation for more information.
View your inboxes in the web app interface. Click the emails tab in the sidebar or view emails within an inbox:

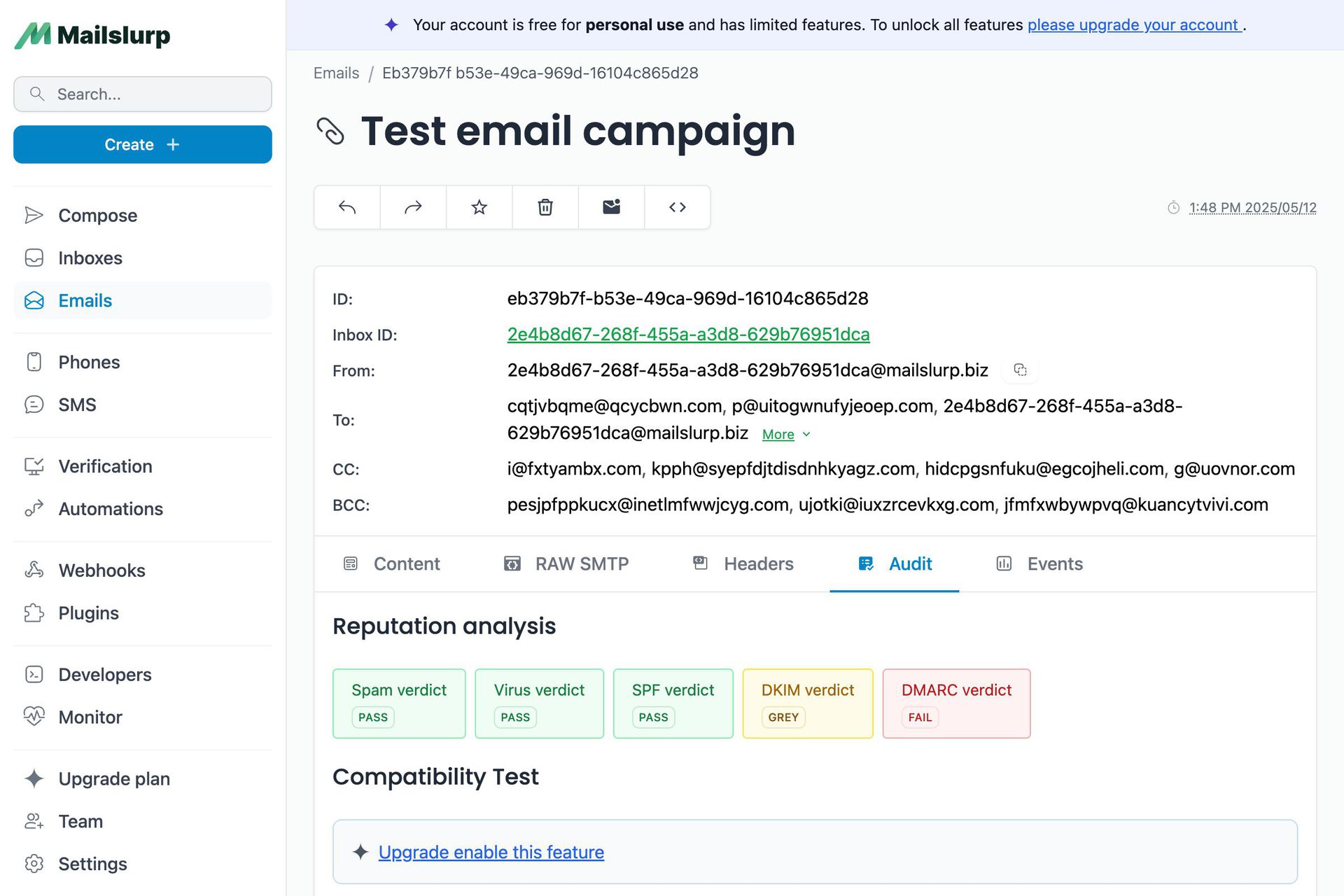
Clicking on an email will open the full message and show the email.

You can also view the raw SMTP message, spam analysis, recipients, headers and more on the email page.
Each email you send creates a sent email entity and a delivery status record. Here is a preview in the dashboard of the sent email page.

Sent emails can be viewed in the dashboard or downloaded using the API.

When an email sending attempt is made the transaction result is saved as a delivery status that contains the SMTP mail server IP address and response status for debugging.

You can see all the sent statuses in the dashboard or using the API endpoints.

MailSlurp can report delivery status and email open events using embedded pixels sent with emails that log opening.
Email templates allow transactional email marketing campaigns with variable replacement. Create templates with moustache variables and then set the field values when sending to replace the variables in the email.
Create an email template in the dashboard or using the API. You can include variables using moustache style templating.
Or in the dashboard:

After creating a template you will see the detecting variables and types:

If you want to use variables in your templates simple wrap each variable in double curly braces:
Send templated emails by passing the and in the send email options API calls:
Or in the dashboard when composing:

Variables can be provided directly or implicitly from contact group and properties.

Emails that are sent to non-existing inboxes can result in email bounce backs. Bounces and complaints negatively affect your sending reputation and can result in account freeze, so it is important to monitor your bounces and respond to them.
The best way to avoid bounces is to verify email addresses and filter out bounced recipients when sending.
To validate as you send and remove bad email recipients use the validate options.
You can also validate ahead of time with email lists with the email validation controller:
Use the bounce recipient filter to remove any known recipients at sending time:
Attachments in MailSlurp are stored separately from emails and can be uploaded and downloaded using an attachment ID. Attachments can be passed as octet streams or base64 encoded strings. Most examples use base64 for easier development.
To upload attachments use the upload attachment method and pass a base64 encoded string for the file content. An array containing an attachment ID will be returned. Use the attachment ID to send the attachment or download it.
See the attachment guide for more information.
Attachments can be sent my passing the attachment ID to the send email options:
Download attachment as base64 like so:
There are other download methods and encodings available on the Attachment controller.
See the inbox configuration guide or developer documentation
Check out our tutorial video series.
Email and SMS guides for automation and testing.
View github project code for multiple languages.
Latest posts from the MailSlurp team.
Test, build, and automate messaging with a free MailSlurp account.