Fetching emails in code
How to receive email in Javascript, Jest, CypressJS and Node. Download and read SMTP messages using MailSlurp REST API clients.
From: Uber Receipts uber.deutschland@uber.com
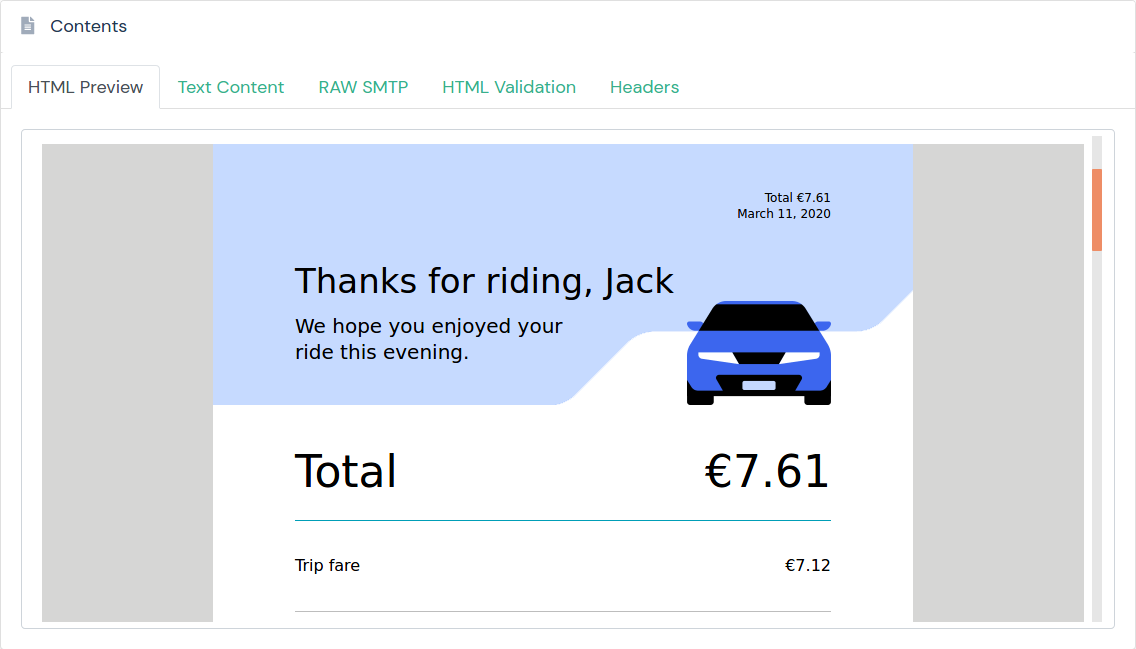
## HTML preview
You can use the [dashboard](https://app.mailslurp.com) to preview HTML emails and attachments visually.
## Special characters
SMTP mail servers can sometimes use arcane encodings for special characters (quoted-printable format for instance). MailSlurp attempts to decode these entities but cannot always do so.
When testing with MailSlurp it helps to view the message bodies in the dashboard or by logging the results. This way you can ensure that expected characters are present in unencoded or decoded form and write code accordingly.
See [quoted-printable article](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quoted-printable) for more information.
## Validations
MailSlurp performs validations on emails so you can check their validity. These include spam anaylsis and HTML validation.
### Spam ratings
MailSlurp analyzes emails to estimate spam detection likelihood and virus verdicts. It also validates SMTP headers for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC validity.

### HTML validation
For HTML emails MailSlurp can validate HTML for symantically correct markup. The results can be viewed in the dashboard:
## Sending emails
Now we know what an email looks like let's send one.
{{<a class="btn-primary mt-6" href="/guides/sending-emails/">}}Next page{{</a>}}